SEO management is all about increasing the quantity and quality of web traffic for your website by improving the company’s online visibility in the organic search results. It aims to improve the business’s ranking on search engines to drive more visitors, generate leads, and boost conversions.
It involves organizing the content of the website by topic that helps Google and other search engines understand what exactly a user is searching for. To demonstrate your expertise in the eyes of search engines, you need to optimize your webpages, not only by topics but also by keywords within those topics. If you’re able to do things correctly, the search engines will rank you well on long-tail keywords.
Table of Contents
1- Terms and Components of SEO
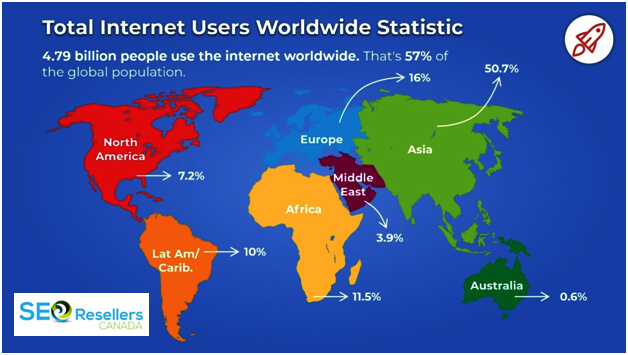
While it’s obvious that web traffic quantity refers to the number of visitors on your website, you might be confused about what the quality of web traffic means.
It’s important to understand that while you can attract just about everyone in the world, you don’t want to do that. Instead, you want users who are genuinely interested in what you’re trying to sell so that they are easy to convert.
Suppose you’re a farmer selling apples and recently started selling via your website. You notice a lot of traffic on your website but the majority of the visitors would leave the site without navigating any further. It turns out, the visitors were actually looking for the brand Apple and Google was directing the traffic to your website. That’s not quality traffic. You need to optimize your website so that only those looking to buy apples online visit your website.
Also, you might be wondering what organic results are. SEO management helps improve your visibility in organic results. If you’ve searched on Google, you must have seen a few results labeled as ‘Ad’? Those are paid results that make a significant part of the Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs). The rest of the results are organic results. This means that SEO helps you target organic traffic, which you don’t have to pay for.
Moving ahead, there are three broad areas of SEO management. We’ll discuss each of them in detail later in the article, but here are some brief explanations for each:
1.1- On-Page Optimization
On-page SEO involves optimizing different elements of your website that impact the search rankings. You use keywords to optimize the content present on webpages to improve their rankings. Following is a checklist of elements you manipulate in on-page optimization:
- Title Tags
- Headings
- URL Structure
- Alt-Text for Images
- Meta Descriptions
- Webpage Content
- Internal Links
- Page loading speed
- Mobile responsiveness
1.2- Off-Page Optimization
Off-page SEO, on the other hand, is all about managing links to your website that are present elsewhere on the internet. Search engine crawler values websites that have links on high-authority websites. Therefore, if you want to improve your website’s search engine rankings, you need to focus not just on the number of backlinks your website has but also the quality of publishers carrying those links.
Based on recent updates on the Google search engine algorithm, having backlinks on low-profile websites can rather cause the ranking to drop, which means that blind link-building tactics are no longer going to work.
1.3- Technical SEO
Optimizing the content and tags on your website is not enough to secure a decent rank on search results. Your website’s architecture or its code is just as important to Google and other search engines as the content. To rank well, you need to have a web developer who will examine the backend of your website and optimize the technical setup of each webpage.
2- How do Search Engines work?

According to Internet Live Stats, more than 3.5 billion Google searches are conducted every day. You may also have thrown hundreds of difficult questions at Google, which magically came up with countless links that may address your queries. But have you ever given a thought to what works behind the search engines to present that long list of results? Understanding how the search engines work will greatly help you in SEO management.
Search engines have crawlers that obtain information about everything that’s present on the internet. They’ll visit webpages and store data they find. The information obtained by these crawlers helps build an index. Whenever a web crawler visits a webpage, it creates a copy of it and includes its URL in an index. It then finds any links on the page, follows them, and keeps on copying, indexing, and exploring the links, thereby establishing a huge index of numerous webpages.
This index is fed through a search engine algorithm that matches the stored data with searchers’ queries. Hence, the results you see on search engines have all been visited by a web crawler.
But why do crawlers need to build an index? This is because Google can’t have a single large database that stores all webpages. In that case, sorting through the content would become extremely slow every time a query is entered. You need to find a shortcut when you have a massive amount of content at your disposal. Having an index greatly simplifies this process.
Search engines use data analysis software such as Hadoop to manage and sort through large amounts of data rapidly. Whenever you put a query on Google, for instance, data analysis software such as Hadoop will manage and sort through large amounts of data in the index. This makes it much quicker than having to search the entire database every time.
To excel in SEO management, you will need to have a clear understanding of how search engine algorithms work and what they value and stay informed about any updates.
2.1- Understanding Search Engine Algorithms
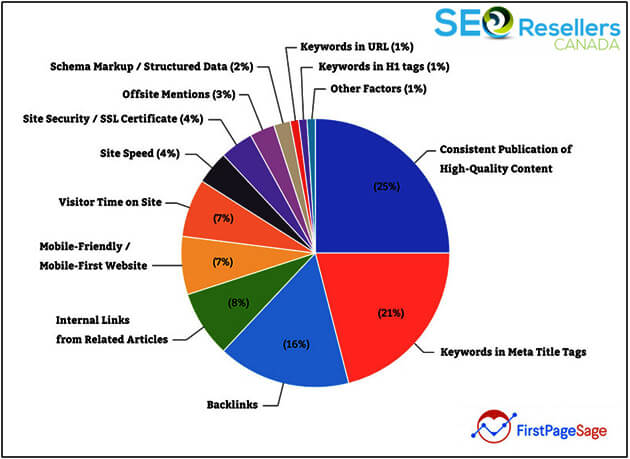
A good search engine will not attempt to present pages that best match your searched query. Instead, they’ll do their best to answer your question. Once the web crawler places a shortcut to a webpage in the index, it can now be found or displayed as soon as a matching search query is entered. Here comes another problem. Google will display thousands of results to answer a particular search query, requiring it to decide the order in which it displays those results. This is where algorithms are used. They are a set of weighted metrics that determine the order in which webpages should be ranked.
You might be thinking that once you know what those weighted metrics are, you’ll be able to adjust those factors, thereby improving your rankings. While that’s true, things aren’t that simple either. What makes things tricky is the correlation and weighting of the major on-page and off-page metrics.
Let’s take a look at an example to clarify this. Suppose you searched for ‘chicken sandwich recipes’ on Google. Its algorithm will immediately weight the relevant pages against the search term. We’ll take 2 simple metrics and see how they might influence each other.
Our first metric is the URL. The search term might form part of a URL such as www.recipes.com/chicken-sandwich.
You can see that the keywords used in the search term can all be found in this URL. Google’s algorithm will take this fact into account in applying weights to metrics.
Our second metric is ‘the page’s backlinks’. There might be plenty of backlinks on the page with the keywords ‘chicken sandwich’ and ‘recipes’. However, Google will attach lesser weight to this metric because if the keywords formed part of the URL, they most certainly will be found in the backlinks.
In contrast, Google may have down-weighted the first metric and have applied more weight to metric 2 if the keywords hadn’t appeared in the URL at all.
Hence, the different metrics Google’s search engine algorithm considers impact each other, with constant fluctuations in their relationships and weightage. On top of that, Google keeps rolling out updates on how the algorithm works. These updates rarely involve changes to the metrics themselves. They are mostly tweaks into the relationship and weighting mechanism between their metrics.
The metrics can be split into the following categories:
2.1.1- Relevance
The most important aspect that search engine algorithms consider is how relevant your content is to the entered query. If your webpage is not relevant at all, it may not even appear in the search results at all. The metric is then used to rank the keywords so that the searcher is presented with the most relevant results possible.
Google’s algorithm considers various on-page and off-page factors to determine the relevance of a webpage. These factors focus on keyword placement, such as in titles or anchor text. Certain metrics are a combination of these. For instance, your relevancy score should be high if the overall domain is considered relevant to the search term.
2.1.2- Authority
Authority has to do with the importance of the webpage. It is often explained in terms of votes. In this context, the links to webpages are considered as its votes. The higher the number of these votes, the better the page will rank. This means that a page with a high number of votes links to your webpage that has only one vote, some of that voting power will be transferred to your webpage. Because your backlink is on a page with a lot of votes (a high-authority page), your webpage may still rank well with only one backlink. This transfer of value between pages is known as page juice or link juice.
However, authority doesn’t work independently from relevance. If the anchor text of your webpage link on another website is relevant to your website, it will bring more weight than a link with a less relevant anchor text. Plus, the relevance of that entire webpage to yours also determines how much value will be transferred.
However, keep in mind that just as high-importance websites help improve your rankings, linking to low-domain authority or low-quality websites can hurt your website’s rankings on search engines, which means that it’s the quality of backlinks that matter rather than the quantity. Therefore, you should know how to do off-page optimization. We’ll discuss that in the following section.
2.1.3- Trust
SEO involves a mix of techniques that focus not just on offering great content and user experience but also on artificially manipulating the order of results on Google. While Google appreciates the former intent, it declares war with the latter. Trust is Google’s anti-spam algorithm that makes it difficult to artificially manipulate the search results. Thus, trust metrics are the most difficult ones to manipulate.
Some of them include the domain of the content and its age. These metrics also rely on the quality of links your webpage has. Linking out to high-domain authority websites, including academic ones with .edu domains, helps your website score well on trust metrics while carrying links to low-authority websites will hurt the trust metrics, lowering your rank on Google search engine.
Since Google is a domain registrar, it can view all the data for different domains. Hence, trust metrics also take into account the number of times a domain has changed hands or the time until the registration expires. You just can’t manipulate those.
2.1.4- Usability
Usability metrics focus on the user experience of webpages in deciding how to rank them. It considers the attractiveness of the content, its visibility, and other aspects that impact the user experience. For instance, a webpage may carry valuable content, but ad placement may hurt the user experience, prompting Google to rank your page lower in search results.
Similarly, the speed at which a webpage loads impacts user experience. Hence, this is a critical factor considered by usability metrics. A webpage that takes too long to load annoys searchers, who need to come back to results to pick a different page. A slow-loading page hurts Google’s image and the user experience it offers, which is why Google doesn’t want to rank them well. It makes use of HTML and Chrome user data to measure the speed of the webpages.
3- How to Get SEO Right?
We’ll now look into how you can manipulate three areas of SEO management:
3.1- On-Page Optimization
On-page optimization begins with keyword research. Remember we discussed that SEO is about getting qualified traffic, that is, users who are looking to buy what you sell and who will likely become your customers. You would only be able to obtain that qualified traffic by ranking well for keywords they’re searching for. When we say ranking well, it refers to appearing at the top of the search results.
Bill Gates made a prediction back in 1996 that “Content is King’, which is proving true with every passing day. Google wants to offer great user experience through great, valuable content. Hence, you will need to optimize the content on your website for the most relevant keywords. To make your content great in Google’s eyes here is all that you need to do:
3.1.1- Keyword Search and Their Use
The process of offering high-quality content starts with identifying keywords or phrases potential buyers use when searching for items on the search engines. It makes sense that the keyword you want to include in your post’s heading and throughout the article should be chosen wisely. Since 90% of SEO revolves around keyword selection, you should spend more time on keyword research than any other on-page SEO factor.
A common misconception about the keyword is that its research and selection is just a one-time task. To stay on top, you need to constantly conduct keyword research and check whether the keywords on existing content are making sense now. Also, be sure to choose the right keywords too.
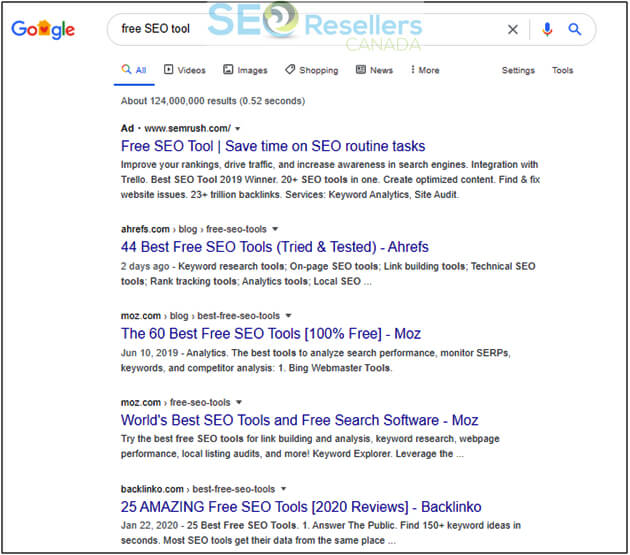
Ranking considerably well for the wrong keywords will take you nowhere as you won’t be attracting the right audience (as seen in the screenshot below). For instance, if you sell an SEO tool that costs $2,000 per month, ranking no. 1 for “free SEO tool” will attract people looking for free stuff. As a result, they’ll immediately leave your site after viewing the subscription packages.
Even though that keyword is bringing in thousands of people to your site, it doesn’t make sense to rank for it. You’d be better off using the right keyword. Even though it may bring fewer people to your website, they are more likely to convert.
When selecting a keyword, you must also take into account the competition. Once you’ve chosen a keyword that aligns well with your business, use a keyword volume tool such as SEMrush or Google Keyword Planner to examine their use and competition. When you enter a keyword in Google Keyword planner, here is how the results will look like:
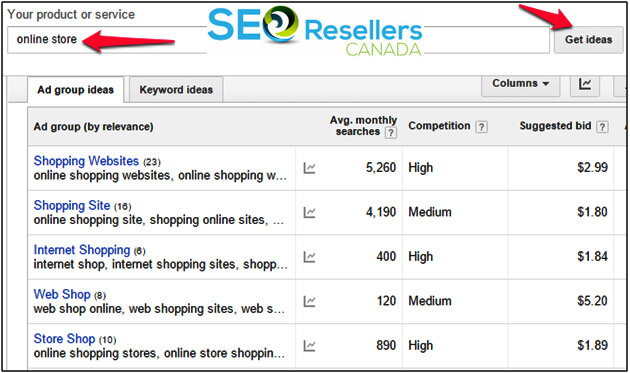
Marketers are often tempted to go for keywords with the highest of searches, not knowing that their ability to rank for a keyword depends on the competition for that keyword. You need to check the sites already ranking for those keywords and compare them with yours. If those sites have a massive number of linking root domains and possess high page and domain authorities, it will take years for you to get anywhere close to them and make it to the top few results on Google.
As an alternative, you might want to choose a long-tail keyword with low volume. The problem here is that keywords with low volume may not necessarily have low competition too. If, for instance, sites that have been around for years, carry hundreds of links for the long-tail keyword, the competition would be just as high as that for a high-volume short keyword. Hence, this approach is even riskier because you’d hardly get any traffic even if you managed to rank well for such keywords.
Hence, your aim should be to choose keywords that are relevant to your business, not too competitive and offer sufficient traffic to achieve your business goals.
The most effective technique in choosing keywords is to focus on the search intent of the users, that is, what exactly will your target audience be looking for?
One great tool to choose keywords is AnswerThePublic, which makes use of actual search queries to build a list of keywords and allows you to identify the people searching for them too.
Plus, the Google search algorithm is now more intelligent than ever. So when it comes to including keywords in your content, you can’t rely on keyword stuffing to manipulate the rankings anymore. You’ll be amazed by how far the algorithm goes to interpret the searchers’ keywords today. For instance, it also looks at the synonyms of the search terms to understand the search intent.
As seen below, when you search for “five guys” on Google, the search knows that you aren’t looking for 5 random guys but the popular fast-food chain, Five Guys, Burgers & Fries, and immediately shows the associated word suggestions in the dropdown.
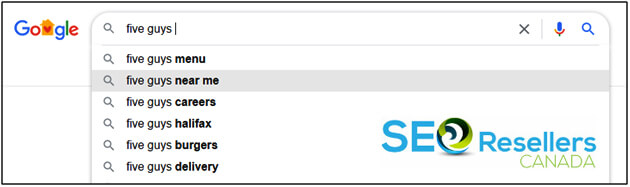
Hence, instead of adding your keyword tons of times in the article, just make sure that it’s included in important areas such as in the URL, heading, meta description, etc. Seamlessly integrating the keyword a few times in the content should be enough.
3.1.2- Fresh Content
Google values fresh content so that the users are provided with the most up-to-date content. Besides, posting new content, updating existing content, and rewriting are other ways to ensure the freshness of content. However, if you keep posting in-depth and thorough content, posting once a month should be sufficient to demonstrate freshness.
3.1.3- Clear Answers
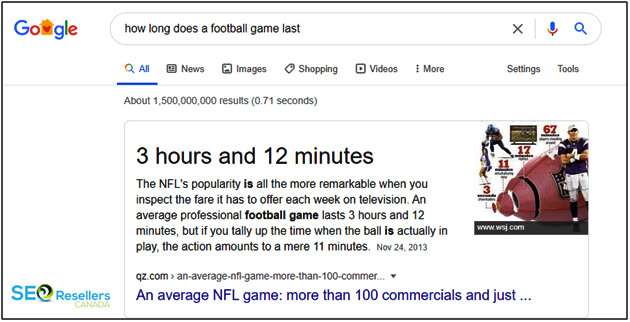
You must have noticed that Google comes up with direct answers to some of your queries. It doesn’t answer on its own but what it finds on webpages around the internet. If your content is clear enough, Google may track answers to particular questions in it and immediately display at the top of the search results when someone enters one of those questions. See an example below:
To be clear enough, you will need to avoid the use of technical jargon and fancy buzzwords as well as ensure simple sentence constructions in your content.
3.1.4- Optimizing the HTML

Once you have optimized your website content with the chosen keywords, you need to handle the HTML right. The term might be scary but honestly speaking, you don’t need to possess programming or coding skills for this. Yet, it’s best to learn about the basics of HTML when running an online business. The following HTML components will need to be optimized:
Title Tags
These are the title of webpages that appear on tabs on browsers when you open a webpage. For blogs, however, the same is referred to as h1-tag. To make the title clear to Google, make sure that every page on your website has one h-1 tag.
This is the 160-character text snippet you see under the title for each search result Google displays to searchers. When you optimize this part, it will not end mid-sentence. Include your keywords in the meta description.
If you have a WordPress website, the best approach is to use the SEO Yoast plugin. This plugin will not only help you edit meta description but also allow you to optimize the metadata for social media platforms, integrate with your Google Search Console so that you can identify and resolve issues on your site, create your XML sitemap, and more.
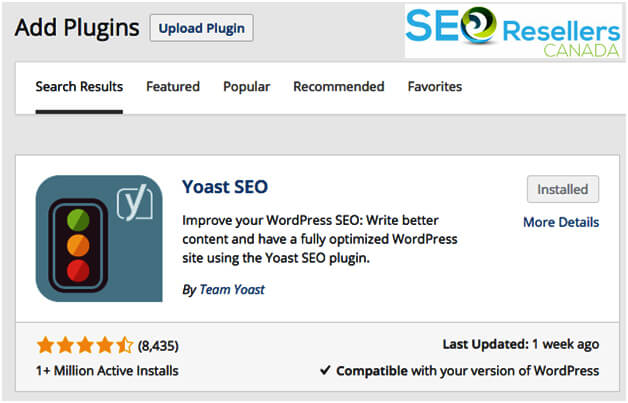
Both the title and meta description can be easily edited through SEO Yoast, as shown below:
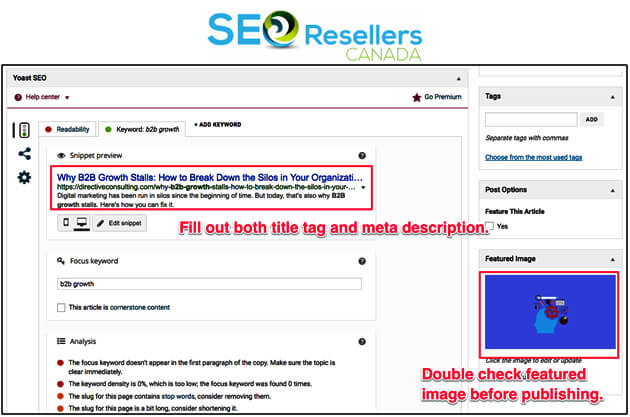
On top of that, Google Search Console will help you diagnose HTML issues and help you improve on them. The report it presents will let you know if you have duplicated your site’s metadata across other pages on your site, if they are too short, and whether they lack keyword intent as depicted below:

Subheadings
Best landing pages will have clearly identified subheadings, which structures your content and improves visibility, thereby impacting SEO. Although h1, h3, h4, etc., are less important than h1 in terms of SEO, they do make some difference.
3.2- Off-Page Optimization
Now let’s look into off-page SEO. The major role in this area is, of course, to create backlinks to your site elsewhere on the internet. There are many ways to get backlinks. No one will create links to your website unless you ask them to do so. We’ve already discussed that your aim should be to build high-quality backlinks as they’re the ones that will help elevate your search engine rankings.
Building high-quality backlinks require you to reach the right sources and giving some value in exchange for the powerful link. An important factor to consider when building backlinks is the anchor text.
3.2.1- Anchor Text

The text the other sites use to create a link to your website is called anchor text, which is important. It may simply be a “click here” link but the more relevant the anchor text is to your website, the more value it will bring from the site, which ultimately impacts your search ranking. The latter ones are referred to as contextual backlinks, which you should be prioritizing on.
3.2.2- Quantity of Backlinks
The quality of links matter, but it doesn’t mean that the quantity has no say at all. At the end of the day, the sites with a higher number of quality links will have an edge over those with lower quality links.
3.2.3- Link to the Right Pages
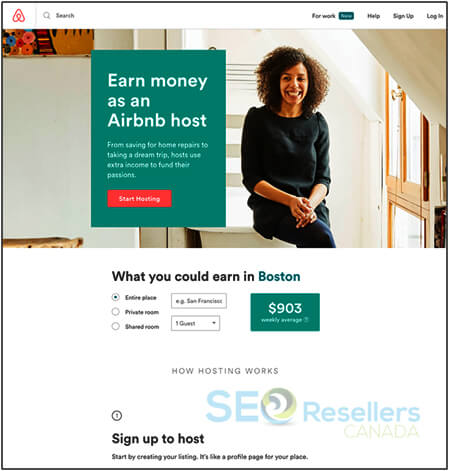
Regardless of whether they are internal or external links, they must be associated with the right pages on your website. While the best links are those directing your homepage, most links will redirect to other pages on your website. Just make sure that landing pages, especially those associated with external links, have something to offer or have a CTA—this means that the visitors can buy something, subscribe, or share their information with you.
Airbnb’s landing page shown below includes a clear call to action at the bottom of the page, making conversions easier.
When it comes to internal links, you may link to other pages such as the privacy policy page, yet you should make sure it gets a link from conversion-related pages.
Keeping the above facts in mind, the following approaches can be used for link building:
Organic, Editorial Links
These links arise from websites that find your content valuable and reference it on their own websites on their own.
Reaching Out Yourself
This strategy involves creating great content and reaching out to high-authority websites via email. If they find your content valuable, they’ll create links to your website.
Guest Posts
This involves publishing blog posts on third-party websites, which allow you to enter 1 or 2 links to your website within the content as well as in the author’s bio.
Including Links on Social Media Business Profiles
You can also incorporate links to your website in your social media business profiles such as in the bio or the content you post from time to time. While they’re easy to build, they don’t carry much authority, which makes them less effective in helping you improve your search rankings compared to backlinks discussed above.
Through all this link-building process, you may want to consider checking your competitors’ links too to get more ideas.
3.3- Technical SEO
Technical SEO involves optimizing elements of the website architecture from the backend to make it easier for Google’s spiders to crawl your website. In other words, it helps make your site more accessible to Google. Google also gives importance to this area because a decent website architecture offers a great user experience in terms of loading times, mobile-friendliness, and safe connection.
We won’t get into the technicalities here, but be sure to avoid duplicate content on webpages and the “404 errors” or broken links, both of which make it difficult for Google spiders to crawl your website.
3.3.1- URLs
The URL for every blog post must include the keywords used in the content, but keep readability in mind when doing this.
3.3.2- HTTPS and SSL
These terms have to do with the security of your website, which Google has become more conscious than ever to rank websites. You must have seen the “insecure” signal Google shows for insecure sites. It prompts users not to enter or share sensitive information with them.
To get around this, you will need to move from an insecure connection to HTTPS or SSL.
Five secure SSL options include Single Domain, Multi-Domain, Wildcard, Organization, and Extended. If you’re yet to buy a domain for your new website, you can purchase these options from your web –hosting service or domain registrar. Otherwise, you can buy one from A2Hosting, WPEngine, or another hosting company. Also, Really Simple SSL, a WordPress plugin can help you with this.
Let’s talk about page-loading speed and mobile-friendliness.
3.3.3- Page-Loading Speed

Long page-loading times can literally kill your conversions. According to Google, if your landing pages takes 7 seconds to load, users are 113% more likely to bounce back from your site. The following screenshot shares more insights:
Start by testing your site speed using Google’s Test My Site tool or Pingdom.
Reduce the Number of Requests: One way to speed up the loading times is to reduce the number of average requests to less than 50. Every time a user enters your web address in the browser, they request your servers to send information. Remember that if the data is huge, the loading speed will be slow. You can compress the information of your pages using GZIP or GIDNetwork.
Reduce the size of your site’s code: The site-loading speed can also be increased by minifying your site’s code. The WordPress plugin, WP Super Minify, will do this for you.
Reducing Image sizes: Large images improve visibility but greatly reduce the site’s loading speed. Before uploading images, use Compressor.io or WP Smush.it. They reduce the size of the images without hurting their visibility.
3.3.4- Mobile-Friendliness
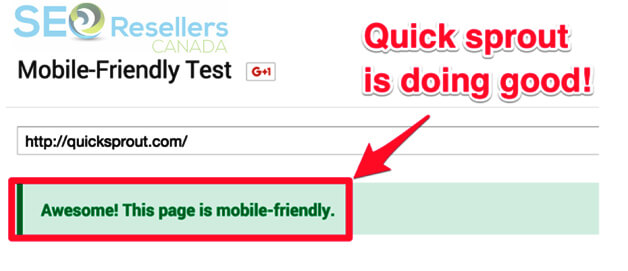
To improve the mobile-friendliness of your site, check the current performance using this Googletool.
Then follow the suggestions given by Google to improve mobile-friendliness. You may also consider buying an appropriate plugin to help with that.
4- Conclusion
By now, you should have a good understanding of how SEO management works and the factors that control the SEO game. Following this guide should greatly improve your online presence. However, there’s no way to get immediate results when it comes to SEO. It will take 6 months or more before you will start seeing results, and that too with consistent efforts.
We, at SEO Resellers Canada, understand the role of SEO in ranking and obtaining traffic to your website. Given the high internet penetration levels across the world, every other business has established an online presence and is looking to make the most out of optimization strategies to rank well on search engines. We can help you stand out from the rest by auditing your website and executing the most effective SEO tactics. Ultimately, you’ll see higher web traffic and more conversions. Contact us today!

























