Back in the early 2000s, SEO was all about filling up your website with as many blog posts and cramming them up with keywords. Today, SEO is slightly more complicated. Search engines have evolved to accommodate human intent, which means you also have to understand what users mean when they type out search queries on Google.
Billions of people make search queries every day. These queries fall into one of three types: transactional, informational, and navigational.
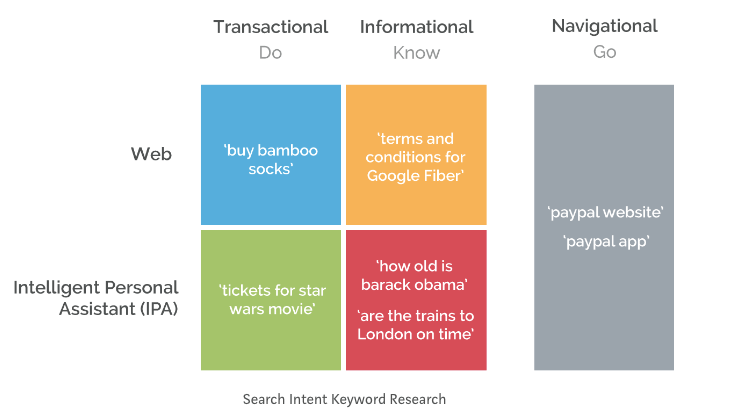
They were first categorized by a scientist at Google named Andrei Broder, who was previously the Vice President of Research for AltaVista. These three search engine categories are designed to codify user intent, which has become the most important tool to understand the meaning behind user behavior.
Before we dive into the three different types of search queries, it is important to explain the differences between them and the roles they play in search engine optimization and pay-per-click marketing.
1- Defining Keywords
Keywords are terms that are based on the products and services you offer. It is easy to rank your website on search engines if you know which keyword to target. For instance, if you run an online gaming store, you might want to rank for “mechanical gaming keyboard” or “the best PC parts in 2020.” The best way to find possible keywords to rank for is with research tools such as Google’s very own Keyword Planner (free) and Moz Keyword Explorer (paid).
2- Hint: Watch out for negative keywords
While it is important to determine what your audience wants, it is equally important to learn what they don’t want. Negative keywords are terms that you don’t want to actively target since it wastes money and resources. For instance, if you are selling ‘gaming mechanical keyboards’ but your visitors want ‘gaming membrane keyboards’, then the term ‘membrane’ is your negative keyword.
You should add as many related keywords to your SEO and PPC campaigns as possible. And just to be extra careful, search for as many negative keywords related to your PPC campaign so you don’t waste your AdWords budget on audiences that will never buy from you.
3- Defining Search Queries
Search queries are what type into the search bar to research about a product, service, or information. Most users would use different ways of typing their search queries into the search bar for the same intent. For instance, if you have 20 users searching for Denzel Washington’s age, those 20 users would type 20 entirely different search terms. These may also include grammar and spelling errors.
4- What Is the Main Difference Between the Two?
The most obvious difference between search queries and keywords is who utilizes them. Businesses optimize their SEO and PPC strategies based on certain keywords. Normally, people type queries they need answers to on Google.
Most consumers aren’t even aware of these terms and don’t think twice about the fact that companies are actively trying to rank for them. They just type what they are looking for and hope that Google or Bing provides them with the right answers.
Businesses must make sense of these search queries to learn which keywords they should target for their SEO and PPC campaigns. In other words, keywords help businesses help people who need products, services, and information.
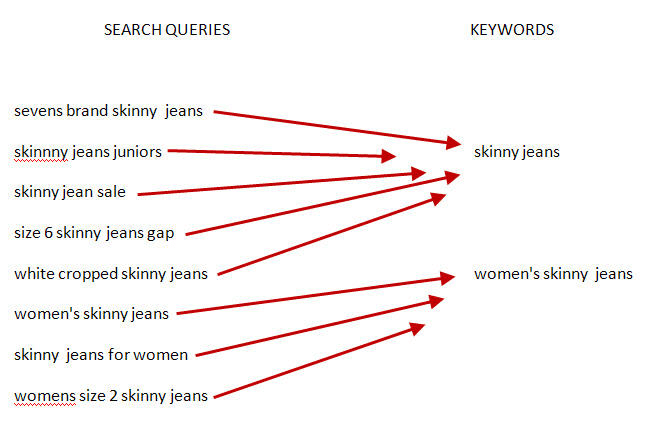
If we were to use the example of mechanical keyboards, there are many variations behind each search query and how they utilize keywords.
Search Queries:
- Best mechanical keyboard
- Gaming mechanical keyboard
- Swappable mechanical keyboard
- Red switches mechanical keyboard
- Tenkeyless mechanical keyboard
Keyword:
It is not possible to target every search query that audiences feed into the search bar since new variations will come up every other day based on the users’ intent.
The end-goal is to find keywords that your users are most likely to use in their search queries and then finding ways to optimize your website to rank higher for them.
If you want to know the difference between the two, then SEO Resellers Canada can help you successfully find keywords based on what users are actively searching for. Visit our website or give us a call today to speak with one of our digital marketing experts!
The Three Main Types of Search Queries
Now, on to the three search queries, we identified earlier in the blog, these are: navigational, informational, and transactional.
4.1- What Are Navigational Search Queries
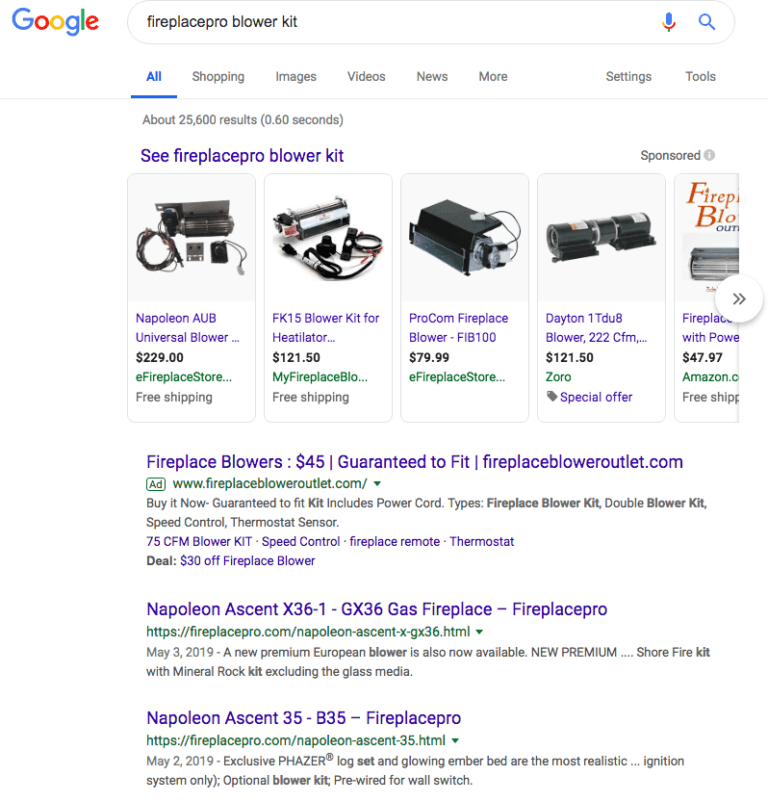
Navigational queries help users find websites and web pages. For example, a user may enter “Toronto sun” into the search bar to find the news site torontosun.com rather than entering the URL directly into the navigation bar. The three top searches on Google as of July 2019 are Facebook, YouTube, and Amazon, and they are all categorized into navigational search queries.
In general, it is not advisable to target navigational queries unless you own the band the searcher is looking for. It just doesn’t make any sense from a purely SEO point of view. Why would you want to rank for, ‘Toronto Sun’ if you don’t own the site anyway?
Besides, even if you start ranking for Toronto Sun on the front page of Google, most users probably won’t click on your URL since this wasn’t their intent. Navigational queries make user intent clear since they know exactly what they are looking for.
That said, not all queries that appear to be navigational are ‘go queries’, as Google puts it. Some users may be typing ‘Toronto sun’ in hopes of learning more about the website from third-party outlets.
It is good practice to target navigational queries for your brand and website. Your website needs to appear in both organic and sponsored results whenever someone types in your name. This is because your profits will end up being higher. Branded keywords are very good at converting leads to high paying clients.
4.2- What are Informational Search Queries
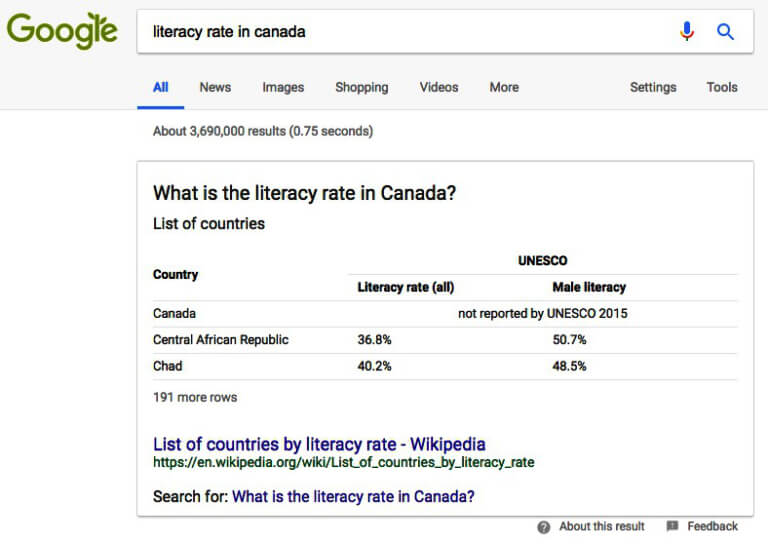
Informational queries are the broadest of the three categories and may include anything a user types to learn about certain topics. For example, “how old is Justin Trudeau,” and “what to look for in a mechanical keyboard?” are informational search queries.
It is clear from these search queries that the user is looking for answers. They usually want one-line answers and aren’t always willing to scrape through endless blog posts in search of answers. Your goal is to anticipate these questions and have the answers ready. Some websites achieve this by creating what is known as an “FAQ” page. This page contains the most commonly asked questions that users pose to their sales team and attempts at answering them immediately.
It is believed that informational search queries make up the bulk of search queries and account for as much as 80% of all searches in both Google and Bing.
While informational queries don’t give you overnight results, they will provide value over time. This is because most users in the research and awareness phase of the buyer’s journey, and by providing relevant information and answers, your website and business become a trusted resource for them.
The best way to rank high for informational queries is to provide optimized, relevant content. Google has rolled out what is known as ‘snippets’, these are special blocks appearing above organic search results and are often described as ‘position zero’. Websites that rank for featured snippets often always rank 1, 2, or 3.
Snippets aim to directly answer the user’s query by capturing the most relevant information from websites. These are all part of Google’s efforts in improving the end-user experience.
The best way to capture Google’s snippets is to create quality content and publish them regularly. Great content requires a deep understanding of your target audience, their goals, and their end goal. Without having the right information, it may be difficult to anticipate informational search queries.
Plus, the featured snippets may completely change depending on the way users phrase their questions.
A good idea to learn about user intent is to research keywords by typing them into Google and Bing. Next, scroll to the bottom of the page to see the ‘related questions’ box. This is where you will find a small list of related queries that people often ask.
To help you with more such information, you can install the “Keywords Everywhere Chrome” extension. This free tool lets you type a keyword into the search bar and then pulls a long list of related queries. Another great tool is “Answer the Public”. Simply type in your keyword and the site will pull up tons of related search queries that users frequently ask for.
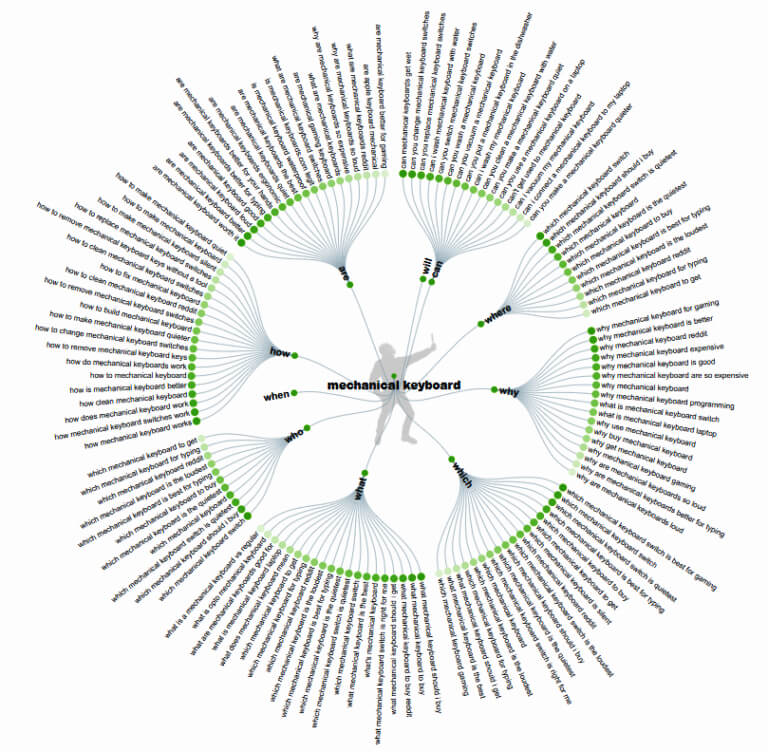
These are the questions that you should build your content around. Focus on articles and blogs full of information, how-tos, and FAQs. If you have the time, try making videos for visual and audio content. The more thorough and in-depth your guides are, the more quickly you will establish yourself as an authority on the subject. Do make sure your content is optimized, you can do this by including the target keywords through the text and headings (without overstuffing them), and even use them in all your images. Once again, the idea is to provide users with information, not flooding their screens with keywords.
4.3- Transactional Searches
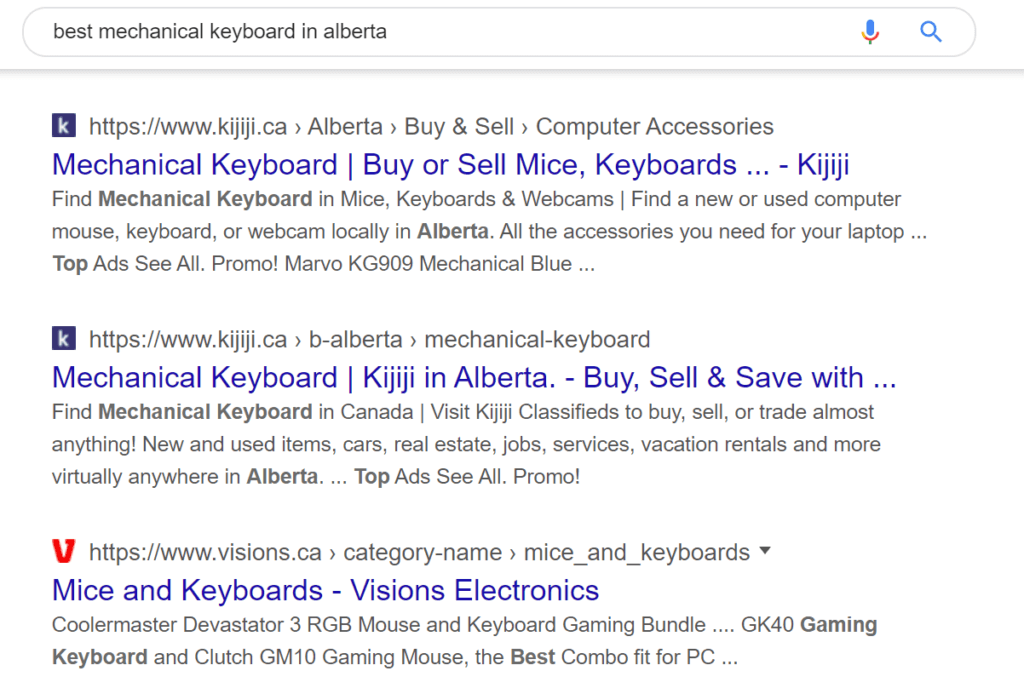
Transactional searches are when the user wants to move further into their Buyer Journey and want to buy a product or service on your website. Think of them as the Holy Grail of SEO. The user using search phrases will include the product’s name specifically in association with words declaring clear intent – such as ‘buy,’ ‘discount,’ and ‘shipping’ – to buy something. Most businesses create landing pages specifically for these keywords and even buy PPC ads for them even if they already rank organically for them. So if you want to go after sales, you want to make content around something like this.
Google recognizes that the user intends to buy something, and it produces shopping results. And if you activated remarketing for your website, Google will show the exact specific product to users based on their previous searches.
Transactional keywords are often described as ‘long-tail keywords’ and are usually easier to rank for than the individual keywords that make them up.
5- Other Types of Search Queries
5.1- Carousel Results
Google Carousel gives businesses a unique opportunity to appear at the top of the search results in the form of a row of images against a white or dark background. Each carousel contains up to 20 results and appears for transactional searches. If you were to type a movie’s name on the search bar only to see a row of images containing names of similar movies, then you’ve already seen what Google Carousel is.
For now, Google Carousel impacts a few industries only including Travel and Hospitality, Restaurants, and of course, Entertainment.
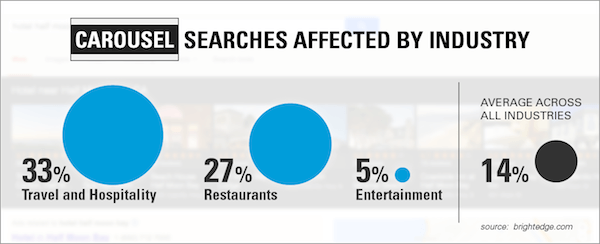
Carousel is a great opportunity to position your business to appear in the first position on more searches. This also means that your business is competing for attention with the 19 or so other businesses that have varying levels of reviews, quality of images, and name recognition. Here are a few things you can do to rank for Google Carousel:
- Set up a Google My Business page.
- Make sure any images selected are unique, high resolution, and ordered in terms of priority.
- Ask happy customers to leave as many good reviews as possible. Your best tool to win over other businesses is to leverage positive reviews.
5.2- Search Ads
When you see Google AdWords at the top, bottom, or side of the page, what you see is a clear indication of commercial intent. In highly competitive environments, paid ads can go hand in hand with your organic results.
5.3- Reviews
Some search terms are more precise than other, more vague terms. This is true in the case of product names. For instance, if you were to type “Bosch 300 Series Dishwasher” or something similar, then the top results will include pages that utilize the review snippet. Google prefers pages that contain reviews and ratings to help users make more informed decisions before buying a product.
5.4- Videos
Certain search queries also snippets in the form of a row of videos, as shown below.
Google gives businesses another opportunity to help them target their search terms. YouTube videos are often easier to optimize for extremely popular search terms than articles and blogs. Most people prefer watching YouTube videos to hear what other people have to say about a certain product or need to see a visual representation of tutorials and in-depth guides.
5.5- Voice Search
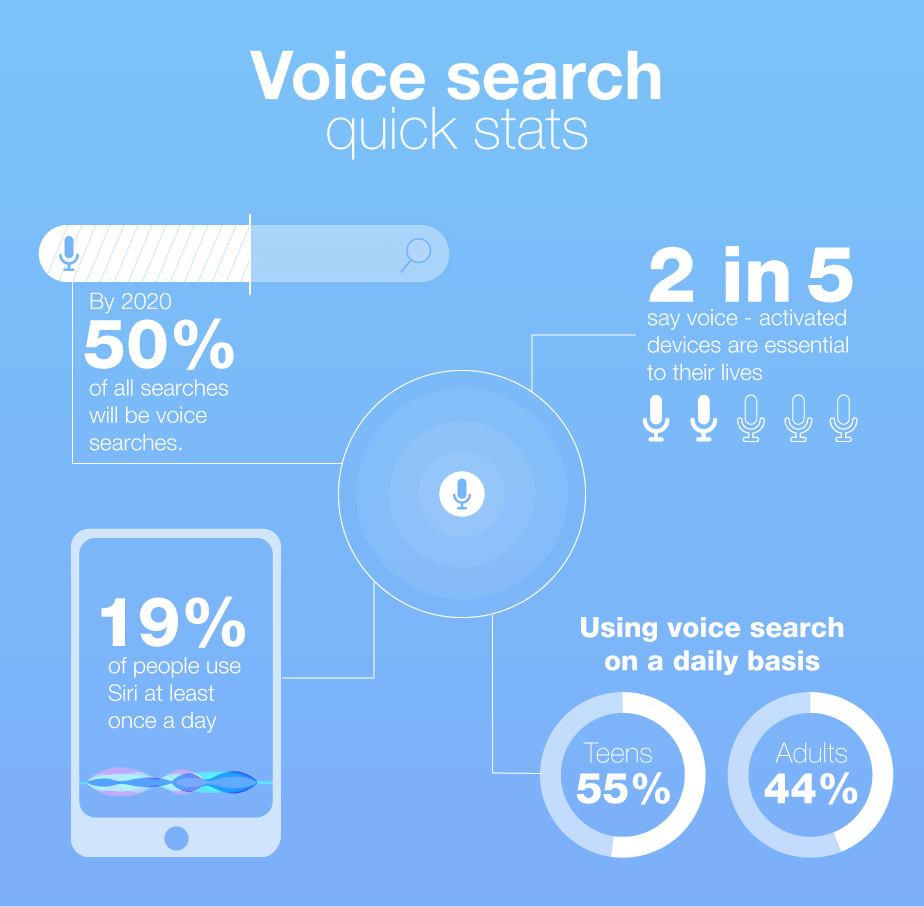
More users are adopting voice search thanks to increased accessibility to microphones in laptops and mobile phones. Google CEO Sundar Pichai confirmed that voice searches account for 20 percent of all mobile queries. Voice search is much faster and convenient for users since they won’t have to type out complex words on their tiny phone screens.
They carefully word their queries and Google fetches the answer from its extensive database, sometimes answering the question directly instead of fetching a search results page. But it’s not just Google that’s tapping into voice search, many tech giants have developed several “digital assistants” to help users. The popular ones include Cortana, Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant.
This allows users to ask questions in a more conversational tone than typing out keywords from their keywords. Since mobile devices now account for over 60% of online traffic, it is in the best interest of companies to optimize their website for voice search.
The best way to rank higher for voice searches is to adjust your content for natural language. This is because most voice search users will not simply ask, “gaming mechanical keyboard,” for example but “look for mechanical keyboards suitable for gaming”. The latter is much longer and informal than is usual for search queries.
A recent study from ComScore found that over 50 percent of searches will be driven by voice in 2020.
6- Selecting Keywords Based on Search Queries
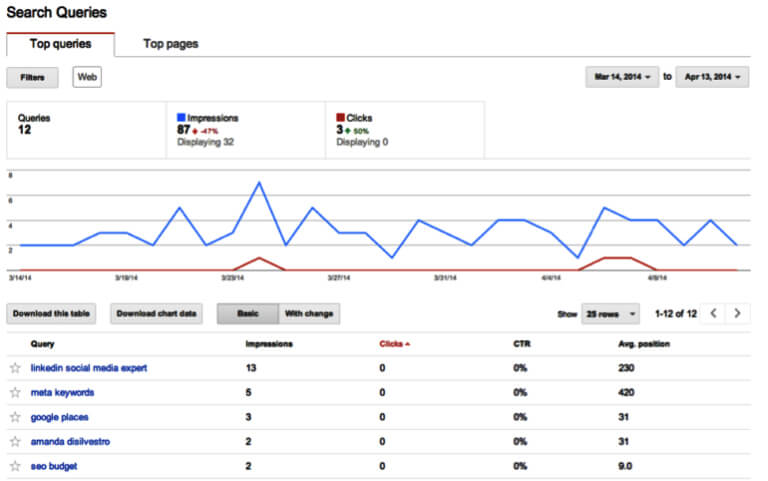
Start by identifying the search queries that will bring users to your site. A good idea is to fetch data from Google Search Console and navigate to Search Analytics. You will then see a list of keywords that brought users to your website in the past couple of days.
This list will give you new ideas for keywords to optimize in your next SEO and PPC campaign. Another common tactic is to type out these words on search engines and then looking to see where your site ranks. If you find that a certain search query is already resulting in a lot of traffic, try creating content for that keyword to help you further capitalize on the results.
The more you improve your rankings for keywords, the more traffic you will attract from users that type related search queries.
Researching Related Search Queries Based on Your Target Keywords
It is good SEO practice to look explore closely related search queries that you are not ranking for. A good idea is to use tools like Ubersuggest. This simple tool lets you type a keyword of your choice into a search bar and then pulls a list of the most common search queries.
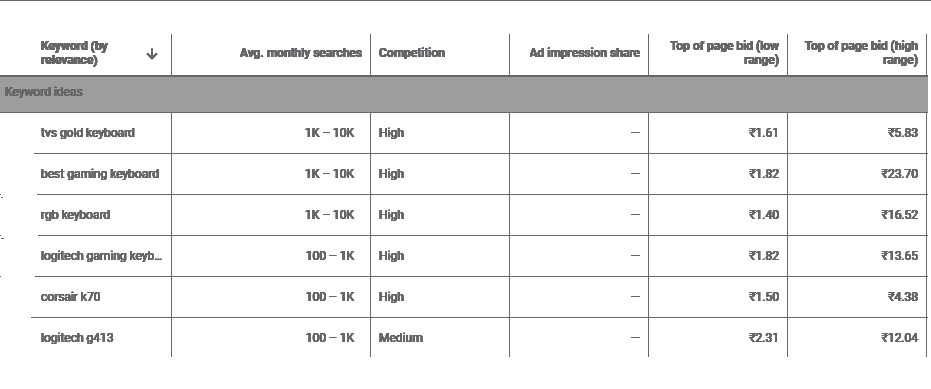
Not all of the search terms on this list will be relevant to your product or services. Another great idea is to use Google Autosuggest to find new search queries. You may have noticed that every time you type something into Google or Bing’s search bar, they almost immediately recommend related terms. Although the accuracy with Google Autosuggest is a hit and miss, most of the time, they are exactly what you should target in your content plan.
These suggestions are loosely based on search queries that other users frequently type. This is a great tool to help speed up the research process for users, but for marketers, you gain a free but valuable insight into what your audiences search for. Google Autosuggest is highly localized, which means the results will vary based on your current location.
Sometimes Google Autosuggest will skew your results based on your search history. To prevent this (and avoid making poor SEO decisions), log out of your Google account and deactivate Web & App activity.
7- Why Should You Care About Search Intent?
As we said in the previous section, your audience’s intent is crucial in how your website does business. It is one of the factors search engines use to affect ranking. It is extremely important to solve the problem a user intended to solve than simply filling up your web pages with jumbled up keywords that don’t make any sense.
Some marketers take keywords at face value, and unfortunately, keywords have different meanings. If someone types “Toronto Sun” together, they may not be searching after the popular website, Torontosun.com, they could be looking for climate and weather-based answers. You have to be extra careful when it comes to interpreting your target keywords.
8- Learn from Your Competitors
Sometimes it helps to learn directly from your competitors and see how they interpret user intent. Their insights will give you a different perspective. As a general rule of thumb, don’t ignore the keywords your competitors don’t seem to care about. Their lack of insight in this regard could be a great opportunity to rank higher on the important search term.
Your end goal should be to create a list of realistic long-tail keywords that will not only provide quick wins but help you build a much larger share.
So how do you figure out what keywords your competitors are ranking for? You can either type out search queries on Google and find out the positions of your competitors directly, or use a tool like SEMrush to see who ranks for the top keywords.
Wondering how to do proper keyword research that accurately accounts for user intent? Get in touch SEO Resellers Canada to talk with experts on how we can help improve your website rankings.





















