There are several actions and conversations simultaneously taking place on the internet, and the most important ones take place when users enter the website URL in their browser to visit it. All that information is then converted into actions and you’re taken to your desired destination.
However, that doesn’t show up on the screen and to understand what’s going on behind the scenes we’re going to be talking about HTTP status codes and SEO to give you a better understanding of what they are and how they impact your website’s SEO rankings on the internet.
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) status codes are the response of the service to the request of the browser. So, whenever you’re visiting a website your browser is going to be sending requests to the service of the website, which will then respond to the request of the browser with a 3-digit code.
That is the HTTP status code and they play a vital role in ensuring that the website server and your browser manage to communicate your requests effectively. There are hundreds of different HTTP status codes that a web server will respond with and that you may encounter in your daily search engine optimization work.

1- How to Check HTTP Status Code
The first thing you should know about HTTP Response codes is that they begin with numbers from 1 to 5 and are presented as 1xx, 2xx, 3xx, 4xx, and 5xx. The numbers belong to the response of the server and they will get more detailed depending on what numbers follow the first digit.
You may already have come across numerous HTTP Response codes when browsing on the internet, and without a doubt, the most common one is the dreaded ‘404’ Not Found code.
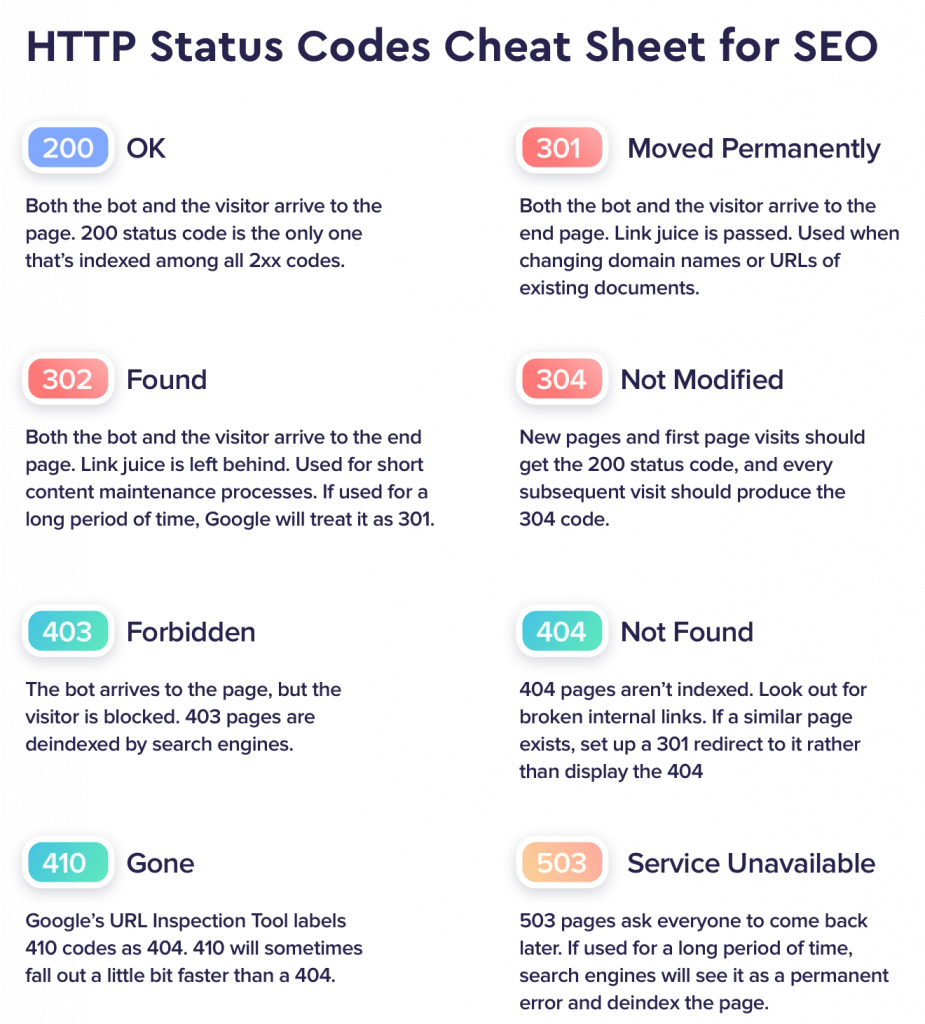
There are various kinds of HTTP status codes and if you’re conducting SEO for a website you must understand them, so you know how to deal with them. That’s why we’re going to be highlighting the most common HTTP status codes you’re likely to come across on the internet. These are as follows:
- 200 – OK
- 300 – Multiple Choices
- 301 – Moved Permanently
- 304 – Not Modified
- 307 – Temporary Redirect
- 400 – Bad Request
- 401 – Unauthorized
- 404 – Not Found
- 410 – Gone
- 429 – Too Many Requests
- 500 – Internal Server Error
- 501 – Not Implemented
- 503 – Service Unavailable
- 550 – Permission Denied
All search engine optimization specialists must know these codes and understand the purpose every response code serves. It’s also important that SEO specialists know how Google and search engines handle these HTTP response codes.
Now that you’ve gotten a fair idea of where these status codes come from it’s time that we dive into one HTTP response code that may give you problems as an SEO professional. That is going to be the ‘410’ – Gone forever status code.
2- The 410 – Gone Forever Code

Whenever you come across 4xx HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) status codes it indicates that an error has occurred with the browser’s request, which has prevented the server to process and complete the request.
A 410 Error Code means that the page has ‘gone forever’, indicating that the page has been removed permanently from the website. The 410 code is close to the 404 Not Found error code, but it’s only used when resources that used to be on the page no longer exist.
3- 410 Status Code

The 410 Response Code is used by web maintenance teams to alert others that a resource has been removed on purpose and all remote links to the page must be taken down. This code is mainly used on limited-time services or promotional pages.
You can also use it for resources that may no longer be linked with a website, and it may end up looking like this:
HTTP was formed to create a way for browsers and servers to communicate with each other on the internet and allow users to access the pages they want to find. HTTP was developed in 1989 by Tim Berners-Lee with CERN and that was when the 410-status code was created.
There are several ways in which you may come across the 410-error code such as, Error 410, HTTP Status 410, 410 Gone, and Gone. When you come across a 410 error it may be suggesting the following:
- There’s a server error and that’s why the server is reporting that the resource has been removed from the website, even though it hasn’t.
- The server may have had a relevant and valid resource at the URL, but the page has since then been taken down intentionally.
- The client may be attempting to request an incorrect resource.
Most people assume that the 410 Status Code error and the 404 Status Code error are the same things, but they are not the same. Google will still revisit a page with 404 codes to check if the page is invalid, but if you use a 410-response code, you’re guaranteed that Google isn’t going to try and revisit that page to check if it’s active.
That’s mainly done so Google can pay more attention to other pages on your website and make it easier for your website crawlers to rank your website higher.
4- ‘410’ Status Code Error Vs. ‘404’ Status Code Error
We’ve already mentioned above that 410 Status Code errors aren’t the same as 404 Status Code errors. The 404 error indicates ‘Page Not Found’, but in most cases,it’s better to use the 410-status code rather than 404-status codes, as they are more informative.
When you use a temporary 410 page, you’re providing search engine crawlers and bots with accurate knowledge and status that they should remove the old link from their crawl index, and that prevents traffic coming on that page.
4.1- Usability Aspect
Looking at it strictly from the usability aspect, using a temporary 410-code is better than redirecting by using a 404-code and if you don’t plan on having that page again on the URL, the 410-code will do the job perfectly. For instance, if your business doesn’t sell a product anymore and doesn’t want to rank for it online, then using a temporary 410-code is going to be better than the 404-code.
You can create a custom 410 page that informs users that you no longer offer a product or service, and to learn more about it by heading over to the main services page. That’s better as users won’t be redirected to an irrelevant page and it will confuse them about what just happened.
4.2- Technical Aspect
When you look at it from the technical aspect, whenever a page issues a 404-response code it informs Google that they can still revisit the page to ensure that it’s invalid. However, with the 410-response code, you ensure that Google doesn’t come back to check on the page and give priority to other pages by improving their search engine ranking.
You should only use the 410-response code when there’s no other option and the page can’t be redirected to another page. So, if you’re certain that a page doesn’t exist and you don’t want traffic coming there, you should use a 410-response code.
5- Fixing HTTP Status Codes
After you’ve listed all the errors, you need to understand why they happened on those pages. It could be due to a consequence of an action that was made by someone or because of an SEO strategy that wasn’t properly planned. Irrespective of where the error is coming from, you’ll need to find a solution for fixing them, and here are some ways you can do that:
- Get in touch with your developers to fix server errors
- Add 410 to pages you don’t want Google to index anymore
- Assign a 301 redirect to the 302 if you don’t want it tobe temporary
- Implement a 404 page with your corporate image and links back to the Home Page to keep visitors browsing on your website.
- You don’t want users encountering a 404, which is why you need to send links directing them to pages that exist.
There are several tools that you can use to diagnose status code errors on any website and minimize their impact on SERPs. Every SEO professional must understand these HTTP status codes so that they can easily analyze the performance of the website and take steps to fix its rankings on the internet.
6- The Importance of HTTP Status Codes for SEO
The objective of search engine optimization is to drive organic traffic that’s going to interest your target market and the general audience. To drive traffic organically to your website, you’re going to need to ensure that your content can be accessed by search engine crawlers. Whenever they request your content, you want the HTTP status to be in the 2xx returned to them. You don’t want to be sending HTTP status codes 4xx and 5xx to them.
Website servers and search engine crawlers communicate with each other with HTTP status codes, and if you don’t understand what they’re communicating, you’re not going to have effective SEO. Not knowing about HTTP status codes when you’re doing SEO is like managing a restaurant in a country where you don’t speak the language. You’re going to see plenty of things going on but you’re not going to know what is going on, why something is happening, and how you can improve it.
7- HTTP Status Codes and SEO Best Practices

A HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) status code is a response message that is sent by the web server whenever a search engine or user attempts to visit a page on the website. The three-digit code indicates whether the request made can be fulfilled or not. To help you better understand, we are going to share how this communication takes place in the following manner:
- The user types the URL of the website and clicks on links taking them to the website
- The browser sends a request to the IP address of the website to retrieve that page
- The server responds with an HTTP status code to provide the result requested by the browser
- If the request is fine, an HTTP 200 code will be sent to the browser and the web page is going to load and become visible to the user
The above steps clearly show how a website page loads and if everything in the process is fine the user will be taken to the respected page. However, if there is a problem with the request, the server will send back an HTTP status code showing an error. For instance, a 404 code may be sent if the page can’t be found and the user will be taken to an error page.
You must monitor the HTTP status codes that are being sent back and forth between your website server and search engine crawlers. That way you can address any issues that come up because leaving them unattended is going to have a negative effect on the indexing and search engine rankings of your website. To help you address problems, here are some SEO best practices you should know:
7.1- Creating a Custom 404 Error Page
You can use a custom 404 error page as a tool to ensure that users don’t leave your website if they don’t find what they were looking for. A 404-error page must have a message that informs the user that the page they requested doesn’t exist anymore.
There should also be a search box on the page, which will help the user search for other products or services listed on the website.
7.2- Redirect 404s Where Necessary
If you want to delete a page from your website with good external links or a page that receives a lot of traffic, you should set up a 301-redirect page on this URL, which will take users to another relevant URL on your website. That will ensure you don’t lose traffic and SEO value associated with that page. However, if your page doesn’t get any traffic or doesn’t have any links pointing to them, or doesn’t offer anything of value to the user, you can use a 404 page.
That will prevent the page from being indexed and crawled by search engines, but you must ensure that any internal links on the page are removed, or else the page is going to continue being found by search engine crawlers. Most SEO professionals believe that you should use a 301 redirect on every page that shows up with a 404 error to the home page of your website.
That doesn’t sound like a good idea on paper because users trying to access the original page may get confused or frustrated when they are taken to the home page instead. That’s why it’s best to inform users that the page they are looking for doesn’t exist anymore on the website.














